Scientists reject the shell of a single battery and replace the cylindrical design with a thin-plate design. The metal sheet is coated with an energy storage material and one side is the positive side. According to the AAA report, US drivers drive an average of 30 miles (48 km) per day, although the electric car charging time is equivalent to three times the number of times, but there are still many people do not want to buy.
 This is the so-called "mileage worries" problem, gasoline cars still dominate the road, mileage concerns are one of the main reasons, but a team of scientists trying to resolve the problem.
This is the so-called "mileage worries" problem, gasoline cars still dominate the road, mileage concerns are one of the main reasons, but a team of scientists trying to resolve the problem.
Mareike Wolter, project manager for the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft mobile energy storage system, is working with a team to study a new battery that allows electric vehicles to recharge for a lifetime of 620 miles (1000 kilometers).
Walter said the project was launched three years ago when the German Institute of Industry and the ThyssenKrupp System Engineering, the IAV automotive engineering researchers, gathered to discuss how to improve the energy density of automotive lithium batteries The They turned their attention to the popular all-electric car Tesla, which began to study.
Tesla's latest car Model S 100D installs a 100 kwh battery pack with a mileage of about 335 miles (540 km). The battery is large, about 16 feet long, 6 feet wide and 4 inches thick. The battery pack contains 8000 lithium ion batteries, each of which is housed in a cylindrical housing with a cylinder of about 2-3 inches (6-7 cm) high and 0.8 inches (2 cm) in diameter.
Walter told Live Science: "We wanted to think that if the space used was the same as the Tesla battery, but the energy density was higher, the mileage could reach 1000 kilometers, that would be a great thing."
She believes that there is a way to achieve the goal, that is, optimize the battery material, so that it stores more energy; In addition there is another way, that is, to improve the overall design of the system.
Approximately 50% of the space of each cell is occupied by components, such as shell, positive, negative, electrolyte (a liquid, let the charged particles move). If you put the batteries into the car needs more space, because the line with the battery and the car's power system connected. "
This design wastes space. "Walter said," there are many inactive components in the system, which, in our view, is a problem. "
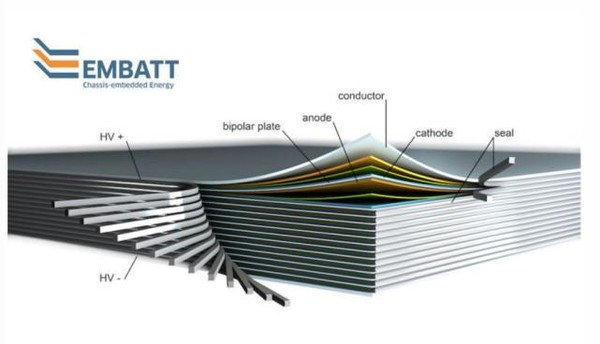
As a result, scientists decided to adjust the overall design of the battery. How to do it? Scientists reject the shell of a single battery and replace the cylindrical design with a thin-plate design. The metal sheet is coated with an energy storage material, which is made of powdered ceramic and polymeric binder. One side of the metal sheet is positive and the other side is negative.
The researchers put the so-called bipolar electrodes one by one stacked, as will be stacked together a sheet of paper, the electrodes separated by a thin electrolyte, there is also a material to prevent charge short circuit. The scientist will then stack the foil in a package size of about 10 square feet (1 square meter), and its upper and lower parts are connected to the car's power system.
The ultimate goal of scientists is to develop a battery system, the size of the space with the Tesla car or other electric car batteries. "We can put more electrodes in the same space and store more power," she said, adding that the researchers' goal was to test the system on the car by 2020.












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite