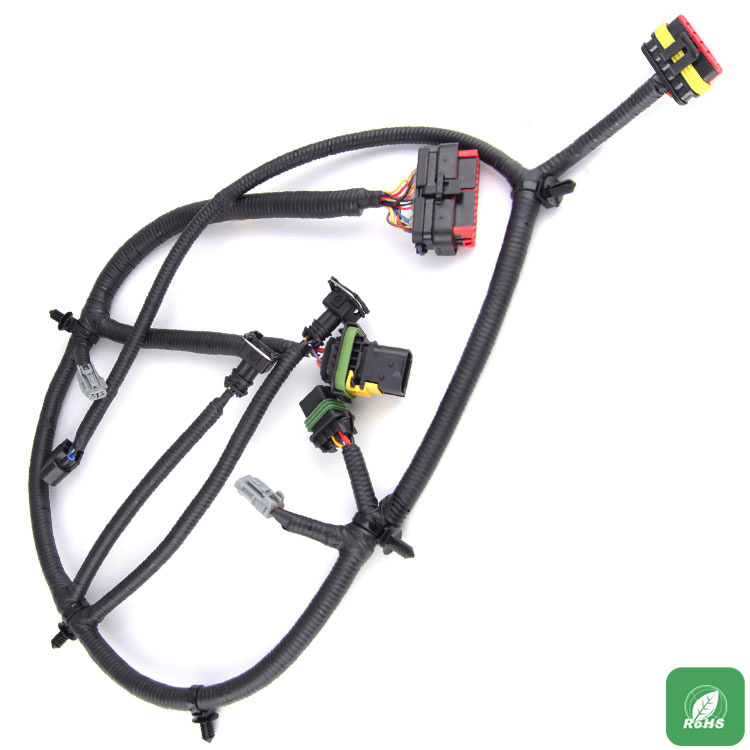
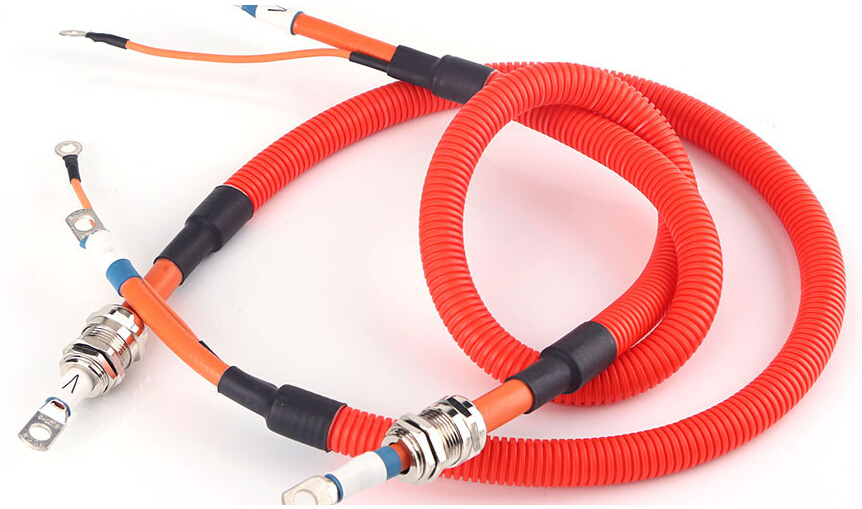
Automobile wiring harnesses, also known as low voltage wires, are not the same as ordinary household electric wires. Ordinary domestic wires are copper single-core wires that have a certain hardness. The car wires are all copper multi-core cords. Some cords are fine, such as hair. Several or even dozens of soft copper wires are wrapped in a plastic insulated tube (PVC) that is soft and not easily broken.
The wires in the automotive wiring harness are commonly used in specifications with nominal cross-sectional areas of 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 4.0, 6.0, and other square millimeters of wire, each of which has a permissible load current value for use with different power consumers. The wire.

Take the vehicle wiring harness as an example, the 0.5 specification line is suitable for instrument lamps, indicator lamps, door lamps, ceiling lamps, etc.; 0.75 specification line is suitable for license plate lamps, front and rear small lamps, brake lamps, etc.; 1.0 specification line is applicable to the steering lamp and fog Lamps, etc.; 1.5 specification lines are suitable for headlights, horns, etc.; main power lines such as generator armature lines, ground lines, etc. require 2.5 to 4 square millimeters of wire.
This refers to the general automobile, the most important is to see how large the current value carried by the wire harness, such as the battery's ground wire, the positive power cord is a dedicated car wire alone, their wire diameter are relatively large at least a dozen Above square millimeters, these "giant" wires will not be incorporated into the main harness.
The wiring harness diagram must be drawn before the wiring harness is arranged. The wiring harness diagram is not the same as the circuit schematic. The circuit diagram is an image that represents the relationship between the various electrical parts. It does not reflect how the electrical parts are connected to each other and is not affected by the size and shape of the individual electrical components and the distance between them. The wiring harness diagram must take into account the size of the electrical components and the distance between them, but also reflect how the electrical components are connected to each other.












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite