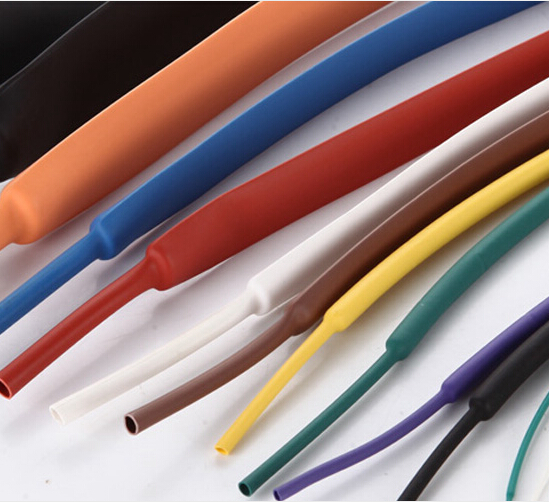
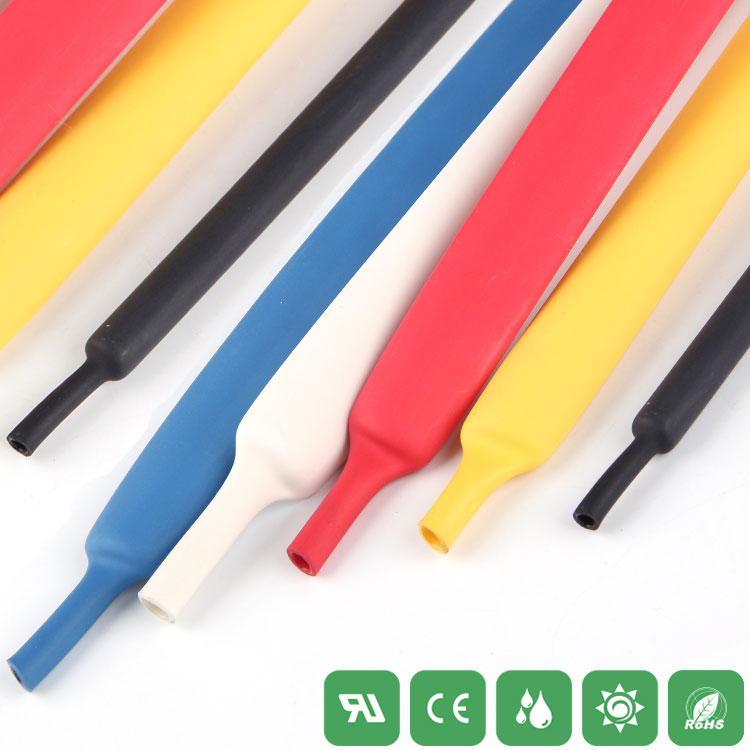
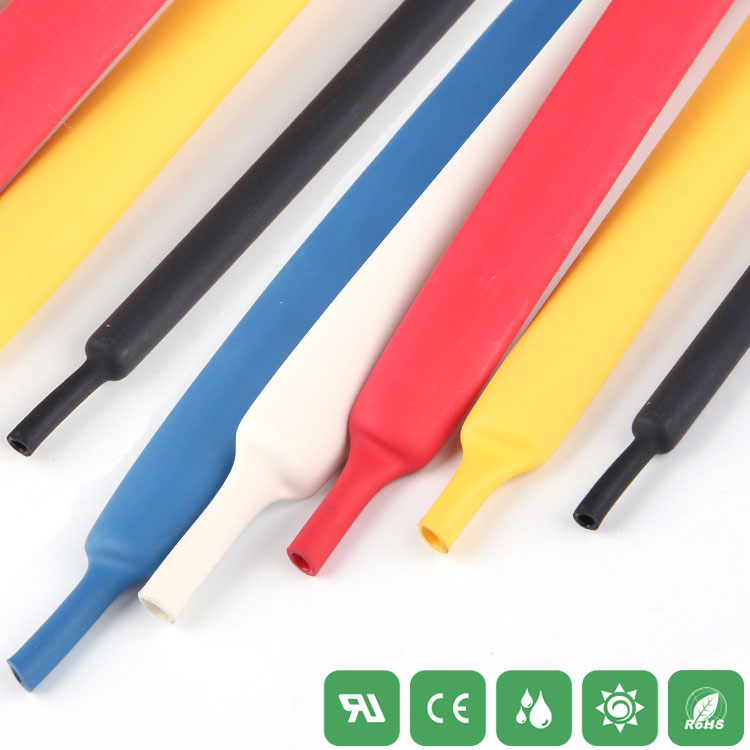
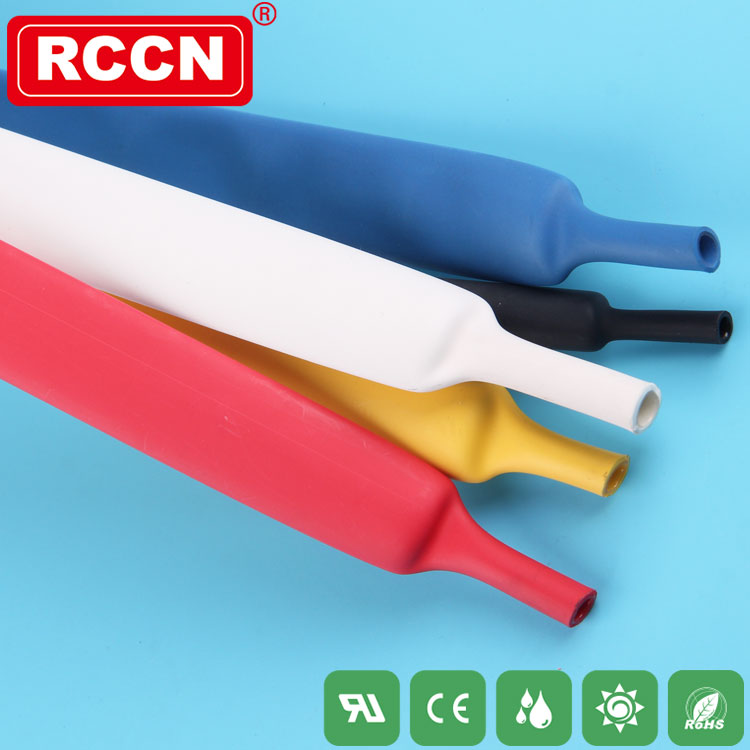
Heat-shrink tubing is not an important component in circuit design, but it is responsible for protecting circuits and important devices in the circuit. However, the protection of the circuit can be maximized by selecting the heat-shrinkable tube according to the appropriate size. In this article, Xiaobian will introduce the basic parameters of the heat shrinkable tube.
Take the PE heat shrinkable tube as an example. Introduce the parameters separately.
1, inner diameter
We know that the cross section of the casing is cylindrical and the inner diameter is the diameter of the inner wall of the pipe, that is, the distance between the inner walls. We usually use the letter Φ, because Φ is used to mark the diameter of the project. Then followed by a number, indicating the value of the inner diameter, the unit is not written by default is MM mm, such as Φ6.
2, wall thickness
The second parameter wall thickness refers to the thickness of the pipe wall, and the inner diameter reflects the size of the pipe. What does this wall thickness mean? Intuitively speaking, it is the thickness of a thing, so what influences the thickness? We know that the function of the heat-shrinkable tube is insulation protection, so the thickness affects the size of the insulation protection. We all know that the clothes are thick, so the cold and warm The role of the clothes is small, the ability to protect the cold is small, so the wall thickness of the heat-shrinkable tube affects its protective ability, so in general, the thicker the heat-shrinkable tube, the better its mechanical protection.
3, shrinkage rate
The heat shrinkable tube will shrink when heated, and only the shrinking thing will have this parameter. The shrinkage rate is sometimes called heat shrinkage rate, heat shrinkage ratio, etc. It refers to the diameter of the heat shrinkable tube at normal temperature, such as Φ6. The diameter after heating and shrinking is Φ3, then the shrinkage rate we refer to is the ratio of the inner diameter of the heat-shrinkable tube before shrinking to the inner diameter after shrinking, that is, 6/3=2/1, this 2:1 It is the shrinkage rate of the casing. The shrinkage rate reflects the shrinkage capacity of the heat shrinkable sleeve. The higher the shrinkage rate, the finer the heat shrinkable sleeve shrinks. If the heat shrinkable tube is Φ6 before shrinking and Φ2 after shrinking, only two millimeters in size, then its shrinkage is 6:2, which is 3:1.

If the contraction is 1.5mm, then the shrinkage rate is 4:1, the common heat shrinkable tube shrinkage rate is 2:1, 3:1, 4:1; when it comes to shrinkage, we will continue to talk about the wall. Thick, like the cowhide ribs, it will be thinner when the wall is stretched, and the wall thickness will be thick after retraction. After the same heat shrinkable tube shrinks, the wall thickness will also increase, which is more important for the heat shrinkable tube. The wall thickness refers to the wall thickness after the heat shrinkable tube is shrunk, because the shrinkage is the state in which the heat-shrinkable tube is protected under the heavy working condition. The heat shrinkable tube shrinkage rate we refer to refers to the radial shrinkage rate because, in principle, for heat shrinkable tubes, it is theoretically not allowed to change longitudinally.
4, shrinkage temperature
On the surface, it is the temperature at which the heat shrinkable tube starts to shrink. We take the heat-shrinkable tube to start heating, and when the heat-shrinkable tube starts to react, it just starts to have the temperature at which the shrinkage is reflected. Our general PE heat-shrinkable sleeve starts to shrink at a temperature of 84 °C and starts to have a shrinkage reaction.
5, shrinking temperature
It refers to the temperature at the end of the contraction, which can make the heat-shrinkable tube reach the temperature of complete shrinkage. For example, our heat-shrinkable tube is heated to 84 °C. It is not like cowhide, I just need to support it to a large, loose hand, cowhide. The ribs immediately bounced back completely and returned to the original state. And our heat shrink tubing is not like this, heating it to 84 °C will not change back to its original shape like a cowhide, our heat shrinkable tube shrinkage is a gradual process, we heat the heat shrinkable tube to 84 °C, it just has a contraction reflection, can not make the heat shrinkable tube completely shrinking, we must continue to heat, heat it to the final temperature, if it is 120 °C, then it can fully shrink.
6, working temperature
This temperature is an important parameter throughout the heat shrinkable tube. The operating temperature is sometimes referred to as the rated temperature, which refers to the normal and continuous working temperature of the sleeve. The first two temperatures refer to the temperature at which the heat shrinkable tube can be contracted. We are still the example of the Φ6 heat shrinkable tube.
The heat-shrinkable tube is slowly heated by a heat gun. When the temperature starts to reach 84 ° C, the heat-shrinkable tube begins to shrink and then shrinks, and then slowly shrinks to Φ5, Φ4. When the temperature reaches the final shrinkage temperature of 120 ° C, the heat-shrinkable tube shrinks completely to Φ3. Tightly shrinking on the object, and then the process of heating is finished. Then, the part of the heat-shrinkable tube is mounted on the air conditioner and the like for normal work, and its normal working environment, for example, our set The normal working temperature of the tube is -55 ° C to 125 ° C, because we know that many times the products will be sold everywhere, some places are relatively cold, some places are hot, then it has a certain scope of application, our The nominal temperature of the product indicates that it can be used normally at this temperature. Once it exceeds the normal use temperature, it may not guarantee the life. It may not work properly. The normal temperature we are talking about here is that the heat-shrinkable tube can play. Insulation-protected, above this temperature does not necessarily work.
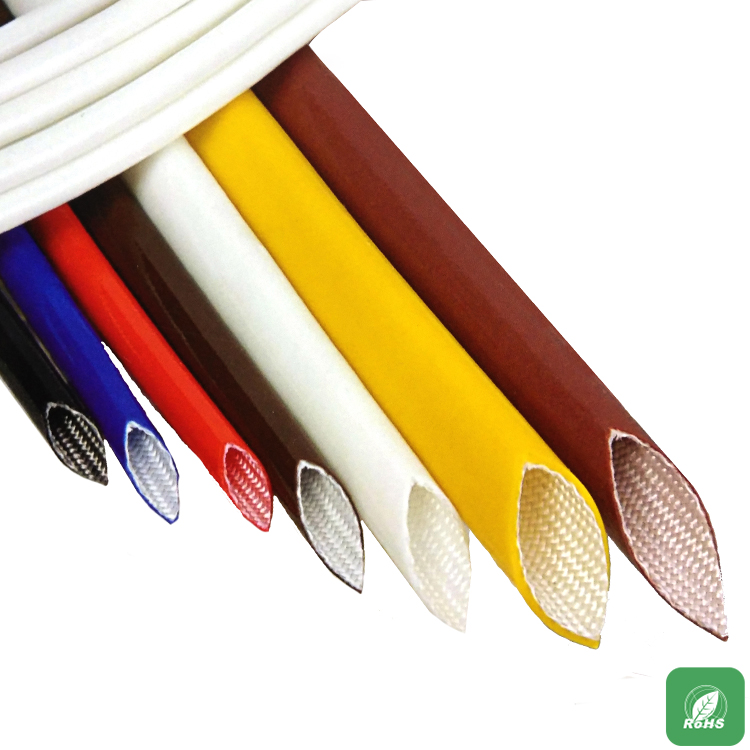
7, color
Needless to say, the color of the heat-shrinkable tube has a regular selection.












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite







