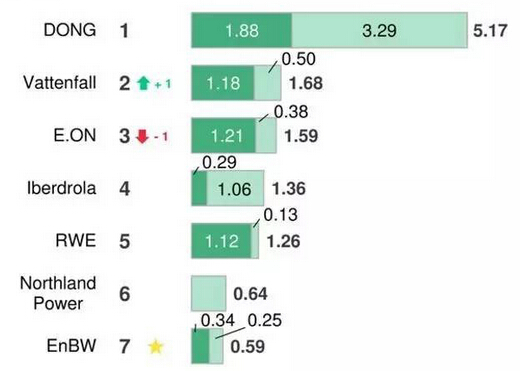
In 2017, the country's newly added grid-connected wind power installed capacity was 15.03 million kilowatts, and the accumulated wind power installed capacity reached 188 million kilowatts. Among them, the grid-connected capacity reached 164 million kilowatts, accounting for 9.2% of the total installed capacity.
In the past few years, many homeowners have improved their power generation by making technical changes to active wind turbines, and investors have achieved good returns.
But the risk of technological change has also followed.
Qin Haiyan, secretary-general of the Wind Energy Professional Committee of the China Renewable Energy Society, said that since the beginning of this year, there have been more and more wind power technology reforms, but some projects lack scientificity in the process of transformation, neglecting safety issues, and this phenomenon is increasingly More, especially need to pay attention.
"There are some extensions of the blade. After more than a year of transformation, there have been problems with blade breakage and even affecting the safety of the unit." Qin Haiyan said.
In fact, as early as 2016, Qin Haiyan has written an article to point out this problem.
He believes that although the current major problems caused by the technical reform of the wind farm are not too many, if continue to continue to develop in accordance with the current situation, there may be major problems that will undermine the stable, healthy and orderly development of China's wind power industry.
The following is an article written by Qin Haiyan in June 2016, "Technology for Power Generation Improvement", the original issue was published in "Wind Energy" magazine. Today, the article's views are still forward-looking.
In the decade since the implementation of the Renewable Energy Law, with the help of the domestic market, China's wind power technology has made great progress. Various innovative technologies have been commercialized and the performance of wind turbines has been greatly improved. Benefiting from large-scale development, practical experience has been rapidly accumulated, which has promoted the improvement of design, improvement of technology, and further improvement of quality and reliability. The rapid advancement of technology has brought about the need and feasibility of upgrading the old organic group. Wind farm owners, machine companies, and third-party technology reform companies have joined the power generation technology as a new business opportunity. At present, many wind power projects have increased their power generation through technological transformation and have achieved considerable benefits.

However, we also found that in these completed technological transformation projects, all parties focused more on the power generation improvement effect brought by the transformation, and ignored the impact on the safety of the unit. Few people conducted scientific safety school. Nuclear and assessment, thus laying a safety hazard. There are many technical transformation methods for power generation improvement. It can start from improving the efficiency of resource utilization, moving the unit to a better resource position; increasing the tower to obtain higher wind speed; introducing sector control to reduce wake impact. It can also improve the performance level of the unit, including: optimization of the main control program, blade replacement or lengthening, replacement of parts, etc.
These means often lead to an increase in load and a mismatch in the system. For example, after some units are raised or moved, the environment and surrounding environment of the unit are changed. Not only the load will increase, but also the wind conditions of other units will be affected, resulting in the fatigue load of other units. Large; after the control strategy is optimized or replaced, the unit may affect the working conditions of the components, resulting in overload work. These safety hazards may increase the unit failure and affect the service life of the unit and components. If it is heavy, it will cause the unit to collapse and cause a major safety responsibility accident. Therefore, after the key technology transformation, a safety assessment must be carried out, and management and technical means should be used to avoid the above problems.
For different optimization and transformation methods, the safety assessment work is also different. For example, for technical transformation projects that change working conditions such as transfer machines, it is necessary to determine the new wind conditions of each aircraft position and compare them with the unit design conditions. If the working conditions exceed the unit design level, the unit load calculation should be carried out. If the load exceeds the unit design load, the limit and fatigue strength of each unit of the unit should be checked; for replacing or lengthening the tower, raising the tower, changing the main control For the unit design optimization project such as the program, the unit control evaluation and load simulation calculation need to be re-executed. If the load becomes larger, the safety evaluation of each part of the unit should be re-executed, and when the design changes are large, such as the blade wing shape change, The blade length changes more than 2%, the rated speed of the unit changes more than 2%, etc., and the type test shall be re-examined according to the relevant requirements of the IEC, including load test, power curve test, safety function test and full-size test of the blade; Auxiliary function modification of radiators such as boxes and inverters, although for the unit Security body has little effect, but also should verify the safety and efficacy rebuilt parts through analysis and testing tools, to avoid small risks lead to big problems.
Safety is a kind of culture. For wind power equipment that needs to operate stably in a complex environment for 20 years, it is more necessary for developers and technical reform subjects to regard safety as a lifeline and give high priority to their thinking. The famous American security engineer Heinrich concluded through a large number of investigations that 88% of industrial accidents can be attributed to human unsafe behavior. Failure to comply with the safety assessment of technical transformation projects is a human unsafe behavior. As a result, the relevant units not only have to pay huge economic costs, but even bear the legal responsibility for safe production. The technical transformation of power generation can not be scientific, and can not be arbitrary. Safety is a necessary prerequisite.












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite