
The first choice is BMC (unsaturated polyester resin glass fiber reinforced molding compound). It can accurately control the size, has good flame retardancy and tracking resistance, has high dielectric strength, corrosion resistance and stain resistance, excellent mechanical properties, very low water absorption and stable color. BMC (DMC) aging resistance Very good, it can be used indoors for 15-20 years, and its strength retention rate is above 60% after 10 years of outdoor exposure. Bulk molding compound (BMC) has excellent flow characteristics, insulation and flame resistance, and is very suitable for various applications that require precise details and dimensions.
PF (phenolic resin is also called bakelite, also known as bakelite powder. It was originally colorless or yellowish-brown transparent material. It is often sold in the market by adding coloring agents to red, yellow, black, green, brown, blue and other colors. There are particles, Powder form. It is resistant to weak acid and weak alkali. It will decompose when encountering strong acid and will corrode when encountering strong alkali.) The electrical performance is unstable. It is highly water-absorbent and easy to crack, so it is not recommended to be used for insulating column products.
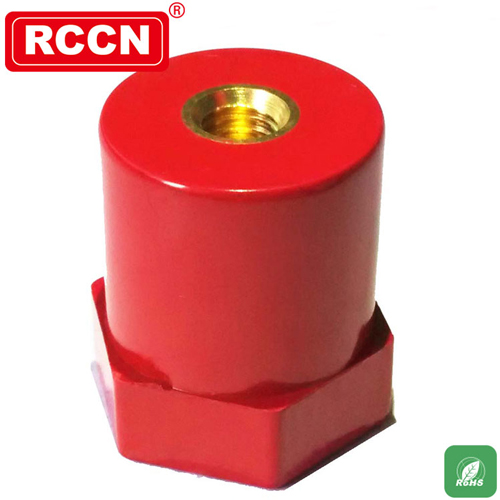
Basic shape combination
It is a cylinder, a hexagonal body, and a truncated cone. The hexagonal body usually functions as a clamping part for installation and tightening. The center of both ends of the cylinder is inlaid with a nut or a screw. Main technical parameters: (different due to material, product shape and processing technology)
1. Working temperature: -40~125℃; (determined by the selected material)
2. Insulation resistance ≥ 500 MΩ; (determined by the selected material and insert spacing)
3. Rated voltage (working voltage): 1500V; (determined by the selected material and insert spacing)
4. Withstand voltage: 3000V .Min; (determined by the selected materials and the spacing of inserts)
5. Breakdown voltage: >30KV; (determined by product material, design and processing technology)
6. Maximum tightening torque: 100 (Kgf.cm); (determined by the selected material, product size and processing technology)
7. Maximum tensile strength; (determined by the selected materials, product size and processing technology)
8. Maximum bending strength; (determined by the selected material, product size and processing technology)
Usually, people refer to items 1 to 4 as electrical parameters, and items 5 to 8 as mechanical parameters;












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite