How to choose robot products and technologies suitable for enterprises? Which method of integration can achieve the highest efficiency? What factors should be paid attention to when purchasing robotic equipment? In the U.S. CONTROL ENGINEERING 2019 Robot Research Report, the interviewees provided us with many references and suggestions on the trends and experience of industrial robots and related software and hardware procurement, robot safety and training, and integration and maintenance.
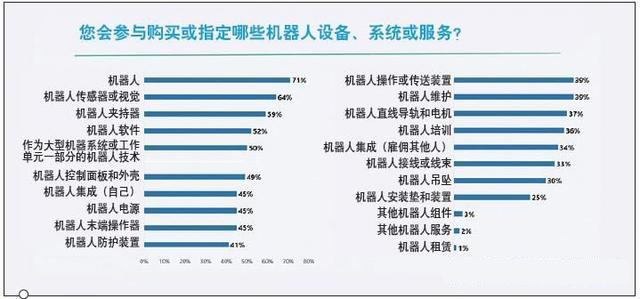
Image source of this article: 2019 CE Robotics Research Report
Which robotic equipment, systems or services will you purchase or specify? 71% of respondents indicated that they purchased or specified robots, 64% of respondents indicated that they specified robot sensors or vision systems; 59% of respondents specified robot grippers; 52% of respondents would purchase robot software ; 50% of the respondents indicated that they would purchase robotic technology as part of a large machine system or work cell; 49% of the respondents indicated that they purchased or specified robot control panels and enclosures.
Robot integration
About 70% of respondents said they would participate in the purchase or designation of robots. Other products and services that will be purchased and developed include robots or vision sensors (64%); robot grippers (59%); robot software (52%); robotics as part of large machine systems or work cells (50%) ), robot control panel and housing (49%). There are also more than a dozen related products or services. The diversity of robot software, training, and components indicates that more extensive engineering design is required when developing robot specifications.
Compared with hiring others to help integrate robots (34%), more respondents will integrate themselves (45%). It seems that robot manufacturers, like other automation suppliers, are making their products easier to set up, program, and operate, perhaps because with population pressure and skill gaps, production time has become a more important indicator. Robot experts can help shorten this time, whether it is employees or robot system integrators participating in the project.
Articulated robots are the most common type of robot (72%). Other common types include collaborative robots, Cartesian robots, gantry robots, mobile robots and SCARA robots.
For open source robot programming software, 27% said they are using or will use it; 31% said they use a controller from a third-party manufacturer to guide the robot to move. 47% of respondents have a material handling/conveying application; 34% of respondents said they have a pick and place application. The current robot mainly uses three types of machine vision: visible light (31%); three-dimensional machine vision (13%); infrared (10%). Machine vision can be used for quality control, palletizing, picking and placement, assembly and other applications.
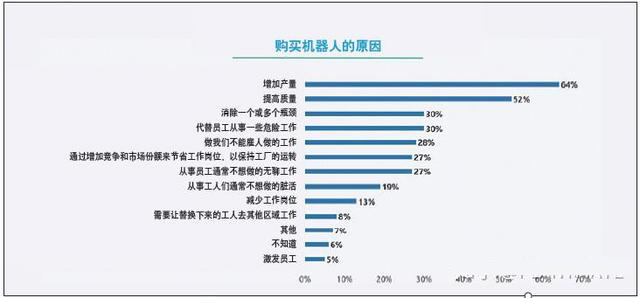
What is your reason for buying a robot next time? 64% of respondents said that their next reason for buying robots was to increase production, and 52% said it was to improve quality.
Robot safety and training
When asked whether most employees involved in robots in your company have received sufficient robot safety training? Although 40% of respondents believe that personnel involved in robots in their facilities have received adequate safety training, more than half of the respondents (56%) believe that they have received insufficient training; 14% of them believe they should get more Robot safety training. 4% of respondents said that the safety risks of robots have not been resolved.
The survey shows that compared with other robot trainers (24%), RIA-certified integrators (21%), RIA Association (17%) and other robot system integrators (13%), consultants and consulting companies provide the most training (54%). Depending on the position, 53% to 70% of people have received sufficient or above-average robot training; 17% to 36% have received the lowest or poorer training, of which robot maintenance personnel received the least training Yes, 36% have received the least or poor training. Robot safety training varies from job to job, with robot maintenance personnel (36%) and robot operators (27%) receiving the least training. This is also the place to be improved in the future.
Robot procurement
Only 12% of companies have one or more scheduled robot suppliers. For procurement or specifications, extremely important decisions include safety equipment (88%), output (87%), avoiding downtime (86%), and quality (86%). Increasing production (64%) and quality (52%) are the biggest reasons for purchasing. Financial support and purchase reasons are the biggest factors affecting purchases (42% each).
More than half of people expect their next robot purchase will be completed within a year. One-third of the respondents said that their next purchase of a robot is within the next 6 months; 4% within a year. 43% of the respondents said that they are willing to consider another supplier for purchasing robots, 32% of the respondents said "probably", and a total of 75% of the respondents may change suppliers.
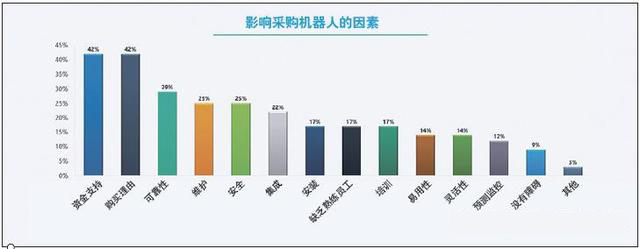
What are the factors that affect the next purchase of a robot? 42% of respondents said that financial support and purchase reasons are the main obstacles to their next purchase of robots; more than 20% believe that reliability, maintenance, safety and integration are the main factors affecting the purchase of robots; 9% of respondents The person thinks that there is no obstacle.
Hardware, peripherals and software recommendations
●Beta testing as much as possible. Keep in mind that once online, it is difficult to troubleshoot.
If you do not test it, it will not work.
●●It is worthwhile to have consistent and efficient programming specifications or programming standards.
●Robot software and peripherals need to be better integrated with other systems.
●The robot needs the support of internal experts; participate in more training so that you have the tools needed to support the entire system. Usually, these items are easy to fix, but only if you experience the pain of struggle from the beginning. All parts of the robotic system must work together, and you must understand them. These skills can be learned.
Robot installation and integration recommendations
●Be careful when evaluating collaborative robot applications. You need to conduct a safety risk assessment of the entire application, including robotic tools and parts to be processed.
●In my humble opinion, regulation is the most critical task.
● Test everything.
●Before purchasing a robot, please use simulation tools to prove the achievable size/payload/cycle time and end effector design.
●Cooperate with system integrators who understand your needs and put safety first. Pay attention to details and don't let yourself fall into a situation of failure.
Maintenance, safety and training advice
●Get more training.
● Obtain training of all relevant personnel from the robot manufacturer.
●Know how to collect data.
●The diagnosis/maintenance, safety and training of the robot are essential.
●Safety first. To meet the challenge, they are the fastest way to become an expert.
●Safety is the number one priority. Never put yourself in a situation where you may be injured by the equipment you install. This may mean making some design trade-offs up front, but it is worth it. Provide your maintenance support with the necessary training to make them successful. Anyone interacting with your system should have a clear understanding of what is allowed and prohibited and how to use the robot safely.












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite